10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2018; 14(11):1558-1570. doi:10.7150/ijbs.24151 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Molecular Alteration Analysis of Human Gut Microbial Composition in Graves' disease Patients
1. Department of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Muhammad Nawaz Sharif University of Agriculture, Multan, Pakistan.
2. Department of Pharmaceutics, School of Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, China.
3. Department of Pharmacology, University of Health Sciences, Khyaban-e-Jamia Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan.
4. Xi'an center for disease control and prevention, China
5. The second Affiliated Hospital of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 157 Xiwu Street, Xi'an China.
6. Department of Endocrinology and metabolic diseases, 1st affiliated Hospital Xi'an Jiotong University, China.
7. Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Key Laboratory of Environment and Genes Related to Diseases of Chinese Ministry of Education, School of Medicine, Xi'an Jiaotong University, Xi'an, China.
Abstract
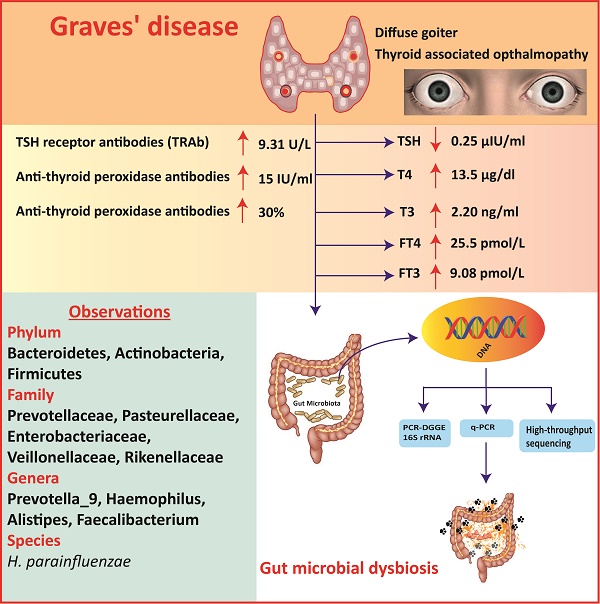
The gut microbial association with host co-existence is critical for body homeostasis and pathogenicity. Graves' disease (GD) is an autoimmune disease manifested with hyperthyroidism and ophthalmopathy. However, we hypothesized that gut bacteria could affect an important role in GD pathogenicity. The current study aim was to characterize and investigate the intestinal bacterial composition of GD qualitatively and quantitatively. 27 GD and 11 healthy controls were enrolled for fecal sample collection. The PCR-DGGE of 16S rRNA gene by targeting V3 region and Real-time PCR for Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, Bacteroides vulgatus and Clostridium leptum, were performed. High-throughput sequencing of 16S rRNA gene with the V3+V4 site was perormed on Hiseq2500 platform on randomly 20 selected samples. The relative analysis of richness indices and diversity illustrated lesser diversification of intestinal bacteria in GD patients in contrast to controls. The data statistics shows the alteration in phyla of GD as compared to control. At the family taxonomic level, the relative abundance of Prevotellaceae and Pasteurellaceae were significantly higher in patients, while Enterobacteriaceae, Veillonellaceae, and Rikenellaceae were significantly lower in the diseased group as compared to control. At the genus level, a significant raised in genera count of the diseased group were Prevotella_9 and Haemophilus, while significantly decreased in the genera of the GD group were Alistipes and Faecalibacterium. The modulation in intestinal bacterial composition was checked at species level particularly H. parainfluenza abundance was raised in GD. The outcomes of the current study are aligned with the proposed hypothesis of gut microbial dysbiosis in GD. Statistically, alpha indices and differential abundance analyses of each intestinal bacterial community were significantly changed in GD. Therefore, the current study may provide a new insight into the GD pathogenesis and, in turn, explore its contribution in possible treatments.
Keywords: GD, Gut microbiota, Ophthalmopathy, Hyperthyroidism, DGGE, High-throughput sequencing

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact