10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2019; 15(13):2783-2797. doi:10.7150/ijbs.35128 This issue Cite
Review
Cyclooxygenase-2 in Endometriosis
1. NHC Key Lab of Reproduction Regulation (Shanghai Institute of Planned Parenthood Research), Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Fudan University, Shanghai 200080, People's Republic of China.
2. Department of Gynecology, Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Fudan University, Shanghai 200011, People's Republic of China.
3. Reproductive Medicine Center, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital, The Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, Jiangsu 210008, People's Republic of China.
4. Clinical and Translational Research Center, Shanghai First Maternity and Infant Hospital, Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai 201204, People's Republic of China.
5. Center for Human Reproduction and Genetics, Suzhou Municipal Hospital, Suzhou 215008, People's Republic of China.
6. Shanghai Key Laboratory of Female Reproductive Endocrine Related Diseases, Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Fudan University, Shanghai 200011, People's Republic of China.
Abstract
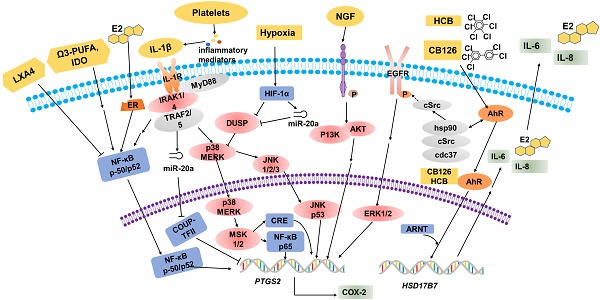
Endometriosis (EMS) is the most common gynecological disease in women of reproductive age, and it is associated with chronic pelvic pain, dyspareunia and infertility. As a consequence of genetic, immune and environmental factors, endometriotic lesions have high cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and COX-2-derived prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) biosynthesis compared with the normal endometrium. The transcription of the PTGS2 gene for COX-2 is associated with multiple intracellular signals, which converge to cause the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). COX-2 expression can be regulated by several factors, such as estrogen, hypoxia, proinflammatory cytokines, environmental pollutants, metabolites and metabolic enzymes, and platelets. High concentrations of COX-2 lead to high cell proliferation, a low level of apoptosis, high invasion, angiogenesis, EMS-related pain and infertility. COX-2-derived PGE2 performs a crucial function in EMS development by binding to EP2 and EP4 receptors. These basic findings have contributed to COX-2-targeted treatment in EMS, including COX-2 inhibitors, hormone drugs and glycyrrhizin. In this review, we summarize the most recent basic research in detail and provide a short summary of COX-2-targeted treatment.
Keywords: COX-2, PGE2, endometriosis, pain, estrogen

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact