10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(1):38-48. doi:10.7150/ijbs.34422 This issue Cite
Review
The Function of Pre-mRNA Alternative Splicing in Mammal Spermatogenesis
1. Key Lab of Swine Genetics and Breeding of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs & Key Laboratory of Agricultural Animal Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction of Ministry of Education, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan 430070, PR China
2. The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan 430070, PR China
Abstract
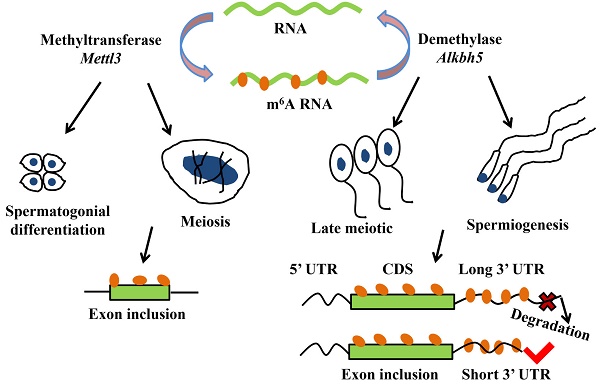
Alternative pre-mRNA splicing plays important roles in co-transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression functioned during many developmental processes, such as spermatogenesis. The studies focusing on alternative splicing on spermatogenesis supported the notion that the development of testis is regulated by a higher level of alternative splicing than other tissues. Here, we aim to review the mechanisms underlying alternative splicing, particularly the splicing variants functioned in the process of spermatogenesis and the male infertility. There are five points regarding the alternative splicing including ⅰ) a brief introduction of alternative pre-mRNA splicing; ⅱ) the alternative splicing events in spermatogenesis-associated genes enriched in different stages of spermatogenesis; ⅲ) the mechanisms of alternative splicing regulation, such as splicing factors and m6A demethylation; ⅳ) the splice site recognition and alternative splicing, including the production and degradation of abnormal transcripts caused by gene variations and nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, respectively; ⅴ) abnormal alternative splicing correlated with male infertility. Taking together, this review highlights the impacts of alternative splicing and splicing variants in mammal spermatogenesis and provides new insights of the potential application of the alternative splicing into the therapy of male infertility.
Keywords: Alternative splicing, Mammal spermatogenesis, Splicing factors, Male infertility

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact