10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(2):194-203. doi:10.7150/ijbs.39024 This issue Cite
Research Paper
Ruxolitinib Alleviates Renal Interstitial Fibrosis in UUO Mice
1. Department of Pathophysiology, College of Basic Medical Science, China Medical University, Shenyang, China.
2. Department of Nephrology, Shengjing Hospital, China Medical University, Shenyang, China.
3. Center of Laboratory Technology and Experimental Medicine, China Medical University, Shenyang, China.
✉ Corresponding author: Chenghai Zhao (E-mail: chzhao@cmu.edu.cn), Department of Pathophysiology, College of Basic Medical Science, China Medical University, Shenyang, China. Tel 86+24+31939318.
Abstract
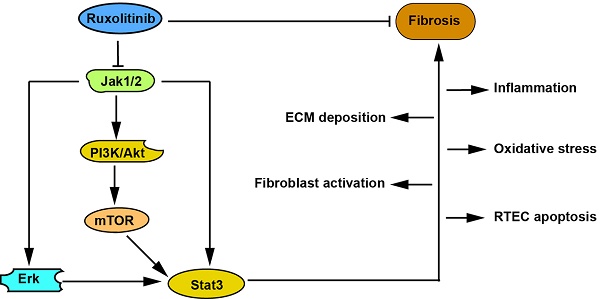
Ruxolitinib is a selective inhibitor of Jak1/2. Downstream signaling pathways of Jak, such as Stat3 and Akt/mTOR, are overactivated and contribute to renal interstitial fibrosis. Therefore, we explored the effect of Ruxolitinib on this pathological process. Unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) models and TGF-β1-treated fibroblasts and renal tubular epithelial cells were adopted in this study. Ruxolitinib was administered to UUO mice and TGF-β1-treated cells. Kidneys from UUO mice with Ruxolitinib treatment displayed less tubular injuries compared with those without Ruxolitinib treatment. Ruxolitinib treatment suppressed fibroblast activation and extracellular matrix (ECM) production in UUO kidneys and TGF-β1-treated fibroblasts. Ruxolitinib treatment also blocked epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in UUO kidneys and TGF-β 1-treated renal tubular epithelial cells. Moreover, Ruxolitinib treatment alleviated UUO-induced inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Mechanistically, Ruxolitinib treatment attenuated activation of both Stat3 and Akt/mTOR/Yap pathways. In conclusion, Ruxolitinib treatment can ameliorate UUO-induced renal interstitial fibrosis, suggesting that Ruxolitinib may be potentially used to treat fibrotic kidney disease.
Keywords: Ruxolitinib, Jak, Stat3, mTOR, TGF-β1

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact