10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(11):1846-1860. doi:10.7150/ijbs.45018 This issue Cite
Review
Initial success in the identification and management of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) indicates human-to-human transmission in Wuhan, China
1. Lab of Chemical Biology and Molecular Drug Design, College of Pharmaceutical Science, Zhejiang University of Technology, Hangzhou, 310014, China
2. Lab of Molecular Immunology, Virus Inspection Department, Zhejiang Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Hangzhou, 310051, China
3. Center for Natural Products Research, Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610041, PR China.
4. Center for Medical Innovation, Nagasaki University, 1-7-1 Sakamoto, Nagasaki 852-8588, Japan.
Abstract
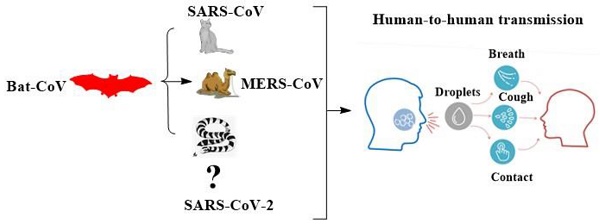
Coronavirus (CoV) has been one of the major pandemic threats to human health in the last two decades. The human coronavirus was first identified in 1960s. CoVs 229E, NL63, OC43, HKU1, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV have caused numerous disasters or human deaths worldwide. Recently, an outbreak of the previously unknown deadly CoV disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome CoV 2 (SARS-CoV-2, early named 2019-nCoV) occurred in Wuhan, China, and it had caused 81238 cases of confirmed infection, including 3250 deaths until March 19, 2020. Its risks and pandemic potential have brought global consideration. We summarized epidemiology, virological characteristics, clinical symptoms, diagnostic methods, clinical treatments, and prevention methods for COVID-19 to present a reference for the future wave of probable CoV outbreaks.
Keywords: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, infection, treatment, prevention

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact