10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(13):2367-2378. doi:10.7150/ijbs.47143 This issue Cite
Review
Kupffer Cells in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Friend or Foe?
1. Guangdong Engineering Research Center of Natural Products and New Drugs, Guangdong Provincial University Engineering Technology Research Center of Natural Products and Drugs, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China.
2. Guangdong Metabolic Diseases Research Centre of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, Guangdong TCM Key Laboratory for Metabolic Diseases, Key Laboratory of Modulating Liver to Treat Hyperlipemia SATCM, Level 3 Laboratory of Lipid Metabolism SATCM, Institute of Chinese Medicinal Sciences, Guangdong Pharmaceutical University, Guangzhou 510006, China.
3. Department of Pharmacy, Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University; 15# Lequn Road, Guilin, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region 54101, China
4. Guangzhou Rainhome Pharm & Tech CO., LTD 5F, No.10 Yongsheng Road, Yonghe Econoic region, Science City, Guangzhou 510663, China.
Abstract
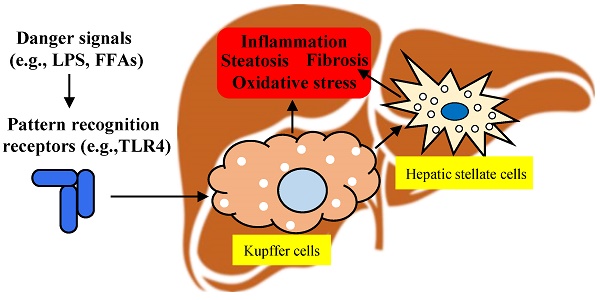
The prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is increasing all around the world and it may become the primary cause of terminal liver disease in adults and children in the next few decades. However, the pathogenesis of NAFLD is complex, and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not approved any drugs for its treatment. Kupffer cells are the key cells regulating immunity in the liver, and the effect of their unique polarization on NAFLD has received increasing attention. Kupffer cells mainly reside in the lumen of hepatic sinusoids and account for 80% to 90% of colonized macrophages in the human body. They are phagocytic cells with the capacity for self-renewal that rarely migrate from their niche in the liver, and play a crucial role in regulating and maintaining homeostasis. Upon liver damage, Kupffer cells will be activated, releasing a good deal of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. This review summarizes the multiple roles of Kupffer cells in the pathogenesis of NAFLD, the role of infiltrating macrophages in the pathogenesis of NAFLD is also briefly discussed, and aims to provide a theoretical basis for designing an NAFLD treatment strategy with Kupffer cells as the therapeutic target.
Keywords: non-alcoholic fatty liver, Kupffer cells, inflammation, lifestyle interventions

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact