10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2020; 16(13):2454-2463. doi:10.7150/ijbs.47142 This issue Cite
Review
Role of Hippo-YAP1/TAZ pathway and its crosstalk in cardiac biology
1. Key Laboratory of Molecular Target & Clinical Pharmacology, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences and the Fifth Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511436, China;
2. KingMed School of Laboratory Medicine, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 511436, China.
*These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
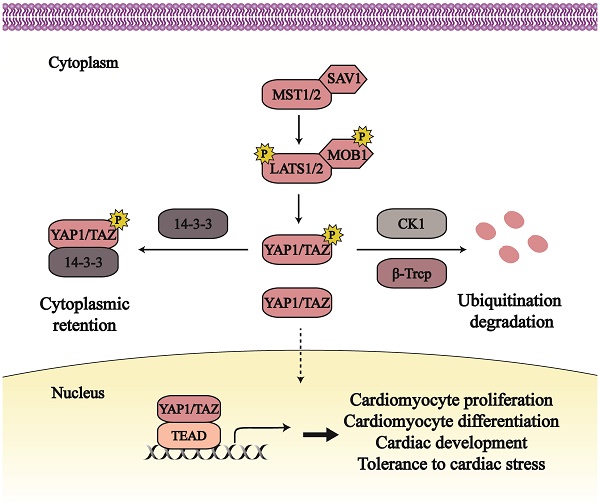
The Hippo pathway undertakes a pivotal role in organ size control and the process of physiology and pathology in tissue. Its downstream effectors YAP1 and TAZ receive upstream stimuli and exert transcription activity to produce biological output. Studies have demonstrated that the Hippo pathway contributes to maintenance of cardiac homeostasis and occurrence of cardiac disease. And these cardiac biological events are affected by crosstalk among Hippo-YAP1/TAZ, Wnt/β-catenin, Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling, which provides new insights into the Hippo pathway in heart. This review delineates the interaction among Hippo, Wnt, BMP and GPCR pathways and discusses the effects of these pathways in cardiac biology.
Keywords: Hippo pathway, Wnt signaling, BMP signaling, GPCR signaling, cardiac biology

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact