10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(3):869-881. doi:10.7150/ijbs.56152 This issue Cite
Research Paper
MLKL inhibits intestinal tumorigenesis by suppressing STAT3 signaling pathway
1. Laboratory of Inflammation and Molecular Pharmacology, Hubei Key Laboratory of Embryonic Stem Cell Research, School of Basic Medical Sciences & Biomedical Research Institute, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, China.
2. Department of Oncology, Affiliated Dongfeng Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, China.
3. State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology, National Cancer Center, National Clinical Research Center for Cancer, Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing 100021, China.
4. Institute of Clinical Pharmacology, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, China.
5. Department of Gastroenterology, Taihe Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Shiyan 442000, China.
Abstract
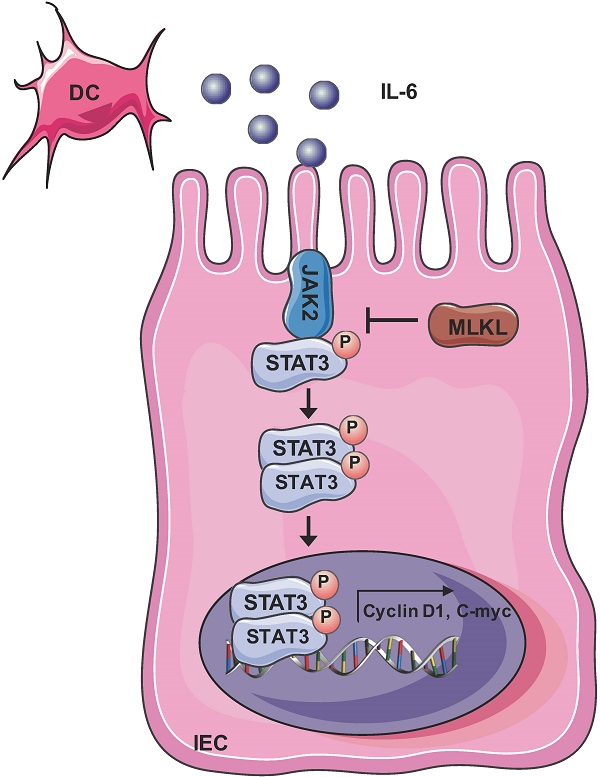
Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) plays an important role in necroptosis, but the role and mechanism of MLKL in intestinal tumorigenesis remain unclear. Here, we found that hematopoietic- and nonhematopoietic-derived MLKL affected intestinal inflammation, but nonhematopoietic-derived MLKL primarily inhibited intestinal tumorigenesis. Loss of MLKL enhanced intestinal regeneration and the susceptibility to intestinal tumorigenesis in Apcmin/+ mice by hyperactivating the Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/ signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) axis. Furthermore, MLKL deficiency increased interleukin-6 (IL-6) production in dendritic cells. Administration of anti-IL-6R antibody therapy reduced intestinal tumorigenesis in Apcmin/+Mlkl-/- mice. Notably, low MLKL expression in human colorectal tumors, which enhanced STAT3 activation, was associated with decreased overall survival. Together, our results reveal that MLKL exhibits a suppressive effect during intestinal tumorigenesis by suppressing the IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signals.
Keywords: Intestinal tumorigenesis, MLKL, IL-6/STAT3, Anti-IL-6R antibody therapy.

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact