10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(9):2323-2335. doi:10.7150/ijbs.60115 This issue Cite
Review
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in pancreatic cancer: Regulatory mechanisms and future direction
1. Department of Pathophysiology, College of High Altitude, Army Medical University (Third Military Medical University), Chongqing 400038, PR China.
2. Department of General Surgery, Air Force Hospital of Western Theater Command, Chengdu 610021, PR China.
3. Department of Cardiology, Southwest Hospital, Army Medical University (Third Military Medical University), Chongqing 400038, PR China.
4. Institute of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery, Chongqing General Hospital, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chongqing 401120, PR China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
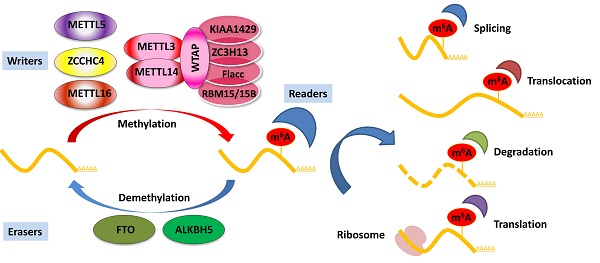
N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most abundant RNA modification in eukaryotes, plays a pivotal role in regulating many cellular and biological processes. Aberrant m6A modification has recently been involved in carcinogenesis in various cancers, including pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest cancers. It is a heterogeneous malignant disease characterized by a plethora of diverse genetic and epigenetic events. Increasing evidence suggests that dysregulation of m6A regulatory factors, such as methyltransferases, demethylases, and m6A-binding proteins, profoundly affects the development and progression of pancreatic cancer. In addition, m6A regulators and m6A target transcripts may be promising early diagnostic and prognostic cancer biomarkers, as well as therapeutic targets. In this review, we highlight the biological functions and mechanisms of m6A in pancreatic cancer and discuss the potential of m6A modification in clinical applications.
Keywords: m6A, pancreatic cancer, RNA modification, clinical application

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact