10
Impact Factor
ISSN: 1449-2288
Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(14):4047-4059. doi:10.7150/ijbs.64628 This issue Cite
Review
Post-Translational Modifications of PCNA in Control of DNA Synthesis and DNA Damage Tolerance-the Implications in Carcinogenesis
1. Institute of Health Sciences, China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, 110122, PR China.
2. College of Basic Medical Science, Key Laboratory of Cell Biology of Ministry of Public Health, Key Laboratory of Medical Cell Biology of Ministry of Education, Liaoning Province Collaborative Innovation Center of Aging Related Disease Diagnosis and Treatment and Prevention, China Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning Province, 110122, PR China.
#These authors contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
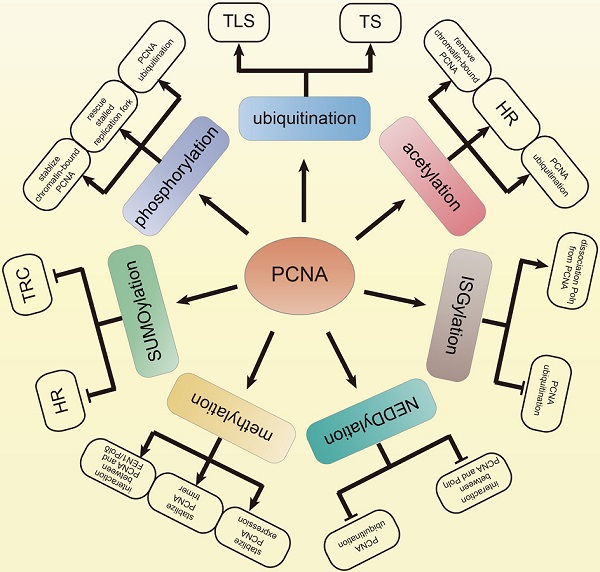
The faithful DNA replication is a critical event for cell survival and inheritance. However, exogenous or endogenous sources of damage challenge the accurate synthesis of DNA, which causes DNA lesions. The DNA lesions are obstacles for replication fork progression. However, the prolonged replication fork stalling leads to replication fork collapse, which may cause DNA double-strand breaks (DSB). In order to maintain genomic stability, eukaryotic cells evolve translesion synthesis (TLS) and template switching (TS) to resolve the replication stalling. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) trimer acts as a slide clamp and encircles DNA to orchestrate DNA synthesis and DNA damage tolerance (DDT). The post-translational modifications (PTMs) of PCNA regulate these functions to ensure the appropriate initiation and termination of replication and DDT. The aberrant regulation of PCNA PTMs will result in DSB, which causes mutagenesis and poor response to chemotherapy. Here, we review the roles of the PCNA PTMs in DNA duplication and DDT. We propose that clarifying the regulation of PCNA PTMs may provide insights into understanding the development of cancers.
Keywords: replication, DDT, ubiquitination, phosphorylation, acetylation, SUMOylation, NEDDylation, ISGylation

 Global reach, higher impact
Global reach, higher impact